The emergence of the Smart Battery System (SBS) greatly simplifies the design of stand-alone battery systems, so its application has surpassed the notebook computer field and appeared in a variety of other applications, such as backup power systems, high-reliability military and aerospace applications. Other key applications include automotive, security/surveillance/anti-counterfeiting systems, medical devices, blade servers, telecommunications and portable electronics.
Smart batteries use internal electronics to measure, calculate, and store battery data, making power usage more predictable. Moreover, smart batteries have an important advantage in that they prevent accidental system downtime.
Smart battery system
A basic SBS system consists of the following: System Management Bus (SMBus), smart battery charger and smart battery.
The modular nature of SBS makes it easy to design a closed-loop battery charging system that allows the use of a battery-independent charger (smart charger) to minimize the cost of non-recurring engineering (NRE) of hardware and software. It also contributes to a rugged system that is especially important for high-reliability battery backup applications. The high-accuracy barometer integrated into the battery pack keeps the battery accurately monitored, even when the battery is not in the system. The barometer is calibrated to the actual capacity of the battery, thus eliminating deviations and ensuring accuracy.
Smart battery charging and protection
The main function of the smart battery charger is for smart batteries
Charging provides a voltage source and a current source. The smart battery communicates with the smart charger via the SMBus interface and optionally communicates with the host. To prevent overcharging due to loss of SMBus functionality, the watchdog timer continues to run to monitor the frequency of calls between the smart battery and the charger. If the battery has been inactive for more than 3 minutes, the charger will pause and wait for the battery to request charging again. In addition, the battery can be controlled by a forced shutdown feature that bypasses the SMBus to provide redundancy and let the charger know that the battery is indeed present.
In summary, the smart battery charger has the following advantages over a fixed stand-alone charger.
1 True plug and play, independent of battery chemistry and battery configuration. Any smart battery pack can be paired with any smart battery charger. Batteries with different chemical properties, configurations, and even different charging algorithms can be replaced with charger circuits without modification.
2 Built-in security features. The SBS standard provides a watchdog timer and a special "safety signal" interface between the battery and the charger.
3 Reliable battery detection system.
4 Automatic charging management, no need for host.
5 Closed loop charging system without host intervention. The host can collect power measurement information as needed.
LTC1760 Dual Smart Battery System Manager
The LTC1760 is a highly integrated three-level battery charger and selector for products that use dual smart batteries. It is a buck switch topology battery charger with a variety of features and other new features that meet the smart battery standard definitions, such as input current limit and safety limits, and more. Three SMBus interfaces enable the LTC1760 to implement servo functions such as tracking the internal voltage and current of two batteries and allowing an SMBus host to monitor the status of any battery. This servo technology enables the accuracy of the charger to be ±0.2% less than the internal voltage and current measurements of the battery.
Traditionally, the dual battery system is a sequential discharge system that allows for sequential consumption of battery power (first draining battery 1 and then consuming battery 2) to simply extend the total battery operating time. The LTC1760 uses proprietary analog control technology that allows two batteries to be safely charged or discharged in parallel. Figure 1 is a simplified schematic of a dual battery system using the LTC1760. This structure increases the charging speed by 50% and the battery operating time by 10%. In addition, parallel discharge not only enhances current capability, but also reduces I2R losses and improves voltage regulation under very high load conditions. Reducing I2R losses and improving voltage regulation all extend the total discharge time of the timing solution (see Figure 2).
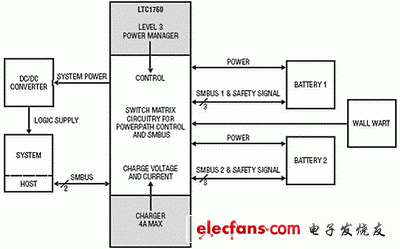
Figure 1 LTC1760 for dual battery system
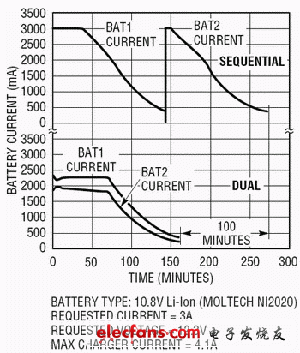
Figure 2 Comparison of battery charging time of dual battery
â— Main features of the LTC1760
1 Independent Level 3 charger polls the battery for charging requirements and monitors the actual current and voltage (with an error of ±0.2%) as determined by the internal battery charge measurement for fast, safe and thorough charging.
2 Fast charging mode can be used to further shorten the charging time.
3 Support battery inspection for barometer calibration.
4 3 power path FET diodes allow safe and low loss simultaneous discharge from DCIN and both cells.
5 Two FET diodes enable both batteries to discharge safely and with low loss.
6 Hardware programmable current and voltage safety limits and many other safety features to complement the battery's internal protection circuitry.
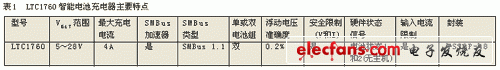
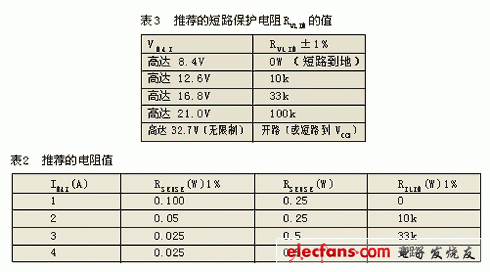
Although the LTC1760 is very precise, it is very easy to use. Only four key parameters need to be determined in any given design: input current limiting sense resistor RICL, current limiting resistor RILIM and matching charge current sense resistor RSENSE, voltage limiting resistor RVLIM, short circuit protection resistor RSC.
The LTC1760 adds some smart batteries and an AC adapter to form a simple system. The system structure is shown in Figure 3.
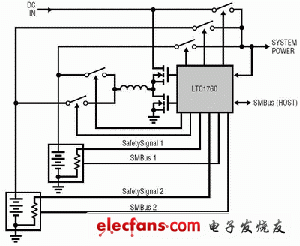
Figure 3 LTC1760 dual battery charger / selector system architecture
â— Input current limit detection resistor RCL
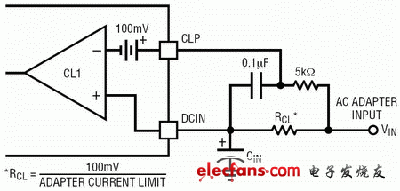
Figure 4 Input current limiting sense resistor circuit
As shown in Figure 4, this circuit limits the charging current to prevent overloading of the AC adapter when system power is increased. To set the input current limit, the most important thing is to minimize the rated current of the wall adapter. The current limiting resistor can be calculated by the following two equations.
ILIM=Adapter minimum current value - (Adapter minimum current value & TImes; 5%) (1)
RCL=100mV/ILIM(2)
However, the AC adapter can have a current limit of at least +10%, so it is often easy to set the adapter current limit to the actual adapter rating.
â— Current limiting resistor RILIM
The RILIM resistor has two functions. First, it tells the LTC1760's SMBus interface that the charger can supply the maximum allowable current of the battery, and any value that exceeds this limit will be replaced by a limit value. The second effect is to synchronize the full-scale current of the PWM charger with the full-scale current limit of the SMBus interface.
â— Voltage limiting resistor RVLIM
The external resistor value connected between the VLIM pin and GND can determine any of the five charger output voltage limit values ​​(see Table 3). This method of realizing the voltage-limiting value in hardware is a relatively safe measure that cannot be replaced by software.
â— Short circuit protection resistor RSC
Each power supply path consists of two back-to-back PFETs in series with the short-circuit sense resistor RSC. The equivalent circuit of the battery power path (PowerPathTM) switch driver is shown in Figure 5.
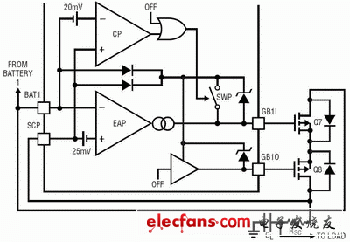
Figure 5 LTC1760 power path circuit
Short circuit protection
The function works in both current mode and voltage mode. If the output current exceeds the short-circuit comparator threshold for more than 15ms, then all power path PFET switches are turned off and the POWER_NOT_GOOD bit is set. Similarly, if the voltage drops below 3V for more than 15ms, then all power path switches will be disconnected and the POWER_NOT_GOOD bit will be set as well. Remove all power supplies to reset the POWER_NOT_GOOD bit. If the POWER_NOT_GOOD bit is set, charging is also disabled.
â— No software required
The LTC1760-based charger does not require software. Placing the integrated circuit in the initial hardware prototype will allow the system to charge and discharge the battery. However, in some cases, you can write some software so that the host can do the following.
1 Collect “charger status†information directly from the smart battery (ie as a barometer);
2 Support battery inspection.
in conclusion
The smart battery system offers advanced features with minimal design work. The LTC1760 is a very comprehensive single-chip dual-smart battery system that is easy to use and requires only four parameters to complete a complete design without the need for software code. The device requires minimal NRE operation to form a complete stand-alone battery charger system and operate normally.
First, Wireless Router
So what is a wireless router?
Wireless router, according to the definition of Baidu Encyclopedia: Wireless router is used for users to access the Internet, with wireless coverage of the router.
A wireless router can be thought of as a repeater that forwards the broadband network signal from the wall of your home through an antenna to nearby wireless network devices (laptops, Wifi-enabled phones, tablets, and all Wifi-enabled devices).
The popular wireless routers in the market generally support four access methods: dedicated xdsl/cable, dynamic xdsl, pptp, and generally can only support 15 to 20 devices online at the same time. It also has some other network management functions, such as dhcp service, nat firewall, mac address filtering, dynamic domain name and so on. The signal range of the general wireless router is 50 meters radius, and the signal range of some wireless routers has reached 300 meters radius.
The name of wireless router can be separated out of two keywords: wireless and routing.
Understand the technical principle behind these two words, you understand the wireless router.
Wireless is also what we often call Wi-Fi. Wireless routers can convert home broadband from wired to wireless signals, and all devices can happily surf the Internet as long as they connect to their own Wi-Fi. In addition, these devices also form a wireless local area network, where local data is exchanged at high speed and is not limited by the bandwidth of home broadband.
For example, many people have smart speakers in their homes that can be used to control various smart appliances. When you say small X small X, turn on the TV, the speaker actually finds the TV through the LAN and sends instructions, and does not need to connect to the Internet; And if you let it broadcast news, you have to get data through the Internet.
The Local Area Network we talked about earlier, also known as the Intranet, is represented by the Local Area Network (LAN) on the router, so the Wi-Fi signal is also called WLAN(Wireless LAN); The Internet we want to access, also known as the extranet, is represented on the router by the WAN(Wide Area Network).
On the Intranet, the IP address of each device is different, which is called a private address. All devices on the Internet share the same public address, which is assigned by broadband operators such as China Telecom Unicom.
The router is the bridge between the Intranet and the external network. The above mentioned IP address translation, packet forwarding, is the router routing function. In other words, the router is the hub of the home network, and the data of all the devices must be forwarded through it to access each other or reach the external network, which means that one husband is the key and ten thousand men are not open, so the comprehensive router is also called "home gateway".
Second, the demand for wireless routers
I do not know if there is a sudden WIFI break when you play games at home, and a stable router is crucial at this time. However, it is important to note that your WIFI frequently dropped may not be a problem with the router, it may also be a problem with the carrier network. (Router means I don't back this pot)
In fact, for most people, there are two basic requirements for wireless routers
Stable and do not drop
Fast Internet and easy setup
Some people will have some advanced needs:
There are some features, USB interface, can be external U disk or hard disk, can achieve simple nas functions, QOS, etc., to advertising and so on
Mesh networking, when the house area is large, multiple routers can be used for Mesh networking
How to choose a wireless router
The wireless router market is in the transition stage from WiFi 5 to WiFi 6, if you want to buy the first choice is definitely WiFi 6 wireless router, which is the future trend.
The speed of WiFi 6 is nearly 40% higher than the previous generation 802.11ac, and the highest connection speed can even reach 9.6Gbps, while the highest speed of 802.11ac is only 6.93Gbp. More importantly, unlike 802.11ac, which only covers the 5GHz band, WiFi 6 covers 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Although the 5GHz band has less interference, it has weak wall penetration ability, and the 2.4GHz band has strong wall penetration ability, which takes into account each other.
So why choose a WIFI6 router?
Compared with the previous generation of 802.11ac WiFi 5, the maximum transmission rate of WiFi 6 in the 5Ghz band has been increased from 3.5Gbps to 9.6Gbps, and the theoretical speed has been increased by nearly 3 times. WiFi 6's 5Ghz single-stream 80Mhz bandwidth can reach theoretical speeds of up to 1201Mbps and 160Mhz bandwidth of up to 2402Mbps.
The band supports 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz.
In terms of modulation mode, WiFi6 supports 1024-QAM, which is higher than the 256-QAM of WiFi 5, and the data capacity is higher. Some high-end WiFi 6 routers support 4096-QAM.
WiFi6 supports MU-MIMO (multi-user multiple-input multiple-output) technology, and supports both upstream and downstream MU-MIMO, with a maximum support of 8T×8R MU-MIMO. The speed is greatly improved. High concurrency, WiFi6 5GHz band, terminal connections up to 128! 5 times that of WiFi5. Effectively solve the Internet needs of multi-person networking and smart home;
WiFi6 adopts OFDMA (orthogonal frequency division multiple access) technology. After using OFDM to parent the channel, the transmission technology of transmitting data is loaded on the subcarrier, allowing different users to share the same channel, allowing more devices to access, with shorter response time and lower delay.
Low latency, WiFi6 time delay can be as low as 10ms, compared to WiFi5 30ms delay, only 1/3. This performance refresh is extremely friendly to game lovers;
If WiFi6 (wireless router) devices need to be certified by the WiFi Alliance, they must use the WPA 3 security protocol, which is more secure.
The WiFi6 wireless router is backward compatible with WiFi5 and WiFi4 terminals.
Fourth, the misunderstanding of purchasing routers
Is the through-wall router really through-wall?
Mistake; The country has strict limits on the transmission power of the wireless router antenna, if you have a lot of rooms in your home, and there are many walls between them, even if you buy an expensive wireless router, you can not do one to cover all the room signals. If the signal is not good, you can consider multiple wireless router Mesh networking.
Does a wireless router have a stronger signal with more antennas?
More antennas just to match the X*X MIMO mode, the more antennas, the more channels, can only ensure that the network is more stable, the impact on the signal is little, the strength of the signal is only related to the wireless transmission power. The wireless transmission power of the country has a standard.
Wifi 5 Wireless Router,5Gz Wifi Router,Wi-Fi Routers For The Home,Lte Modem Router
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommtech.com